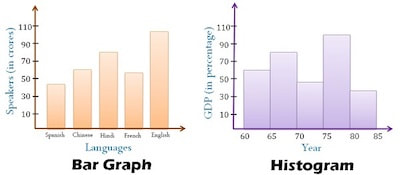
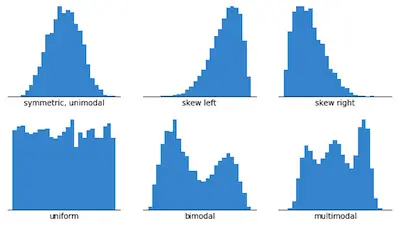
When you look at a glance at a graph with bars, it may look like you are looking at a bar graph when you are looking at a histogram. The truth is that they are both very similar but there is a huge feature that sets the difference between the two. The reality is that in bar graphs, the bars are always separated by continuous intervals. However, in histograms, this doesn't happen and the bars are always touching. Besides, it is also worth to mention that in a histogram, the x-axis is measured in ranges to define various parts of the data.
When To Use Histogram
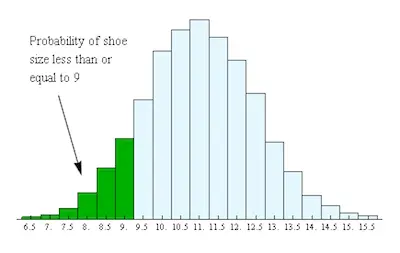
One of the things that you need to know about histograms is that they are an excellent way of describing numerical x-value data. Here's an example: graphing the height of several merchants on the x-axis versus weight on the y-axis. But why should you use a histogram? Well, the reason is that the x-values have arithmetic values.
Learn to make a histogram.
Learn to make a histogram.
Usually, bar graphs are used when relating uncompromising data, and histograms are used when linking arithmetical data. At times when not sure of what to do with a big set of measurements shown in a table, you can use a histogram to arrange and display the data in a more user-friendly and understandable format. It makes it easy to see where most of the values fall in a measurement scale, and how much difference there is. It is also helpful to create a Histogram when you want to perform the following activities.
So, when you need to summarize large data sets graphically, you should use a histogram since it will be a lot easier to understand. Besides, when you need to compare process results with specification limits, you can do it easily with a histogram. This way, you will be able to quickly know if the current procedure was able to produce good products. The specification limits may be the length, weight, density, the quantity of the materials to be delivered, or any other that may be crucial for the product of a given process.
Are you trying to construct a histogram?
So, when you need to summarize large data sets graphically, you should use a histogram since it will be a lot easier to understand. Besides, when you need to compare process results with specification limits, you can do it easily with a histogram. This way, you will be able to quickly know if the current procedure was able to produce good products. The specification limits may be the length, weight, density, the quantity of the materials to be delivered, or any other that may be crucial for the product of a given process.
Are you trying to construct a histogram?
In what concerns to communicate information graphically, a histogram is very intuitive for everyone. Besides, a histogram is also a great tool to help you in decision making. However, and even if you use a histogram, it is important to always make sure that the data that you have in hand is current. When it isn't or you simply don't know how or when it was collected, you shouldn't even consider wasting time trying to chart it.
Discover all you need to know to construct your histogram.
Discover all you need to know to construct your histogram.
Benefits Of Using A Histogram
- When you use a histogram, you will be able to improve your decision-making process since it will be easier to view the data graphically.
- A histogram allows you to display the frequency of occurrences of data within an interval.
- When you use the data that is displayed in a histogram, you can regulate statistical information.
- A major benefit of histograms is that they allow you to determine trends.
- You can use a histogram to make your picture clearer to read and to categorize your data into many diverse classes.







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed