5S
5S is an important Lean Six Sigma waste elimination method which contributes to continuous improvement. This methodology was developed in Japan and actively used by Toyota Motor Corporation. 5S is a method focused on effectively organizing a work space. Although the origins of the 5S methodology are in manufacturing, it can be applied in software development, information and other fields.
5S method consists of the 5 following phases:
5S method consists of the 5 following phases:
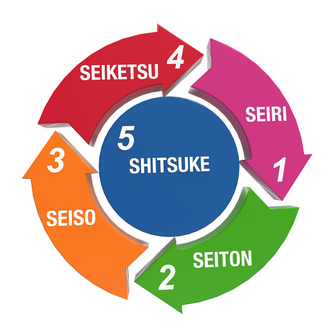
Sort (Japanese: Seiri)
Sort through everything in each work area and remove materials, tools, supplies and equipment which are not frequently used. Use red tags to label the means of production which are not frequently used and place them in a separate storage.
Straighten or Set in Order (Japanese: Seiton)
Arrange all necessary means of production (tools, materials etc.) in order, so they can easily accessed as needed in a production process. If means of production are in right order and readily available, employees will not waste time on looking for them.
Shine (Japanese: Seiso)
The objective of shinning is to maintain a work space neat and safe. Shining prevents machinery and equipment from deterioration. Working in a clean work space increases probability of noticing malfunctions in equipment machinery, such as leaks, vibrations, and breakages.
Standardize (Japanese: Seiketsu)
Once the first three phases are implemented, it is crucial to create a standard approach to maintain high standards of housekeeping and work space organization. In this phase sorting, straightening and shining duties are assigned to regular job responsibilities.
Sustain (Japanese: Shitsuke)
Sustain phase is about institutionalizing good practices and maintaining correct procedures. This phase is crucial for ensuring continuity of waste elimination efforts. Ultimate goal is to standardize effective production processes, so over time workforce develops and maintains effective work habits.
Sort through everything in each work area and remove materials, tools, supplies and equipment which are not frequently used. Use red tags to label the means of production which are not frequently used and place them in a separate storage.
Straighten or Set in Order (Japanese: Seiton)
Arrange all necessary means of production (tools, materials etc.) in order, so they can easily accessed as needed in a production process. If means of production are in right order and readily available, employees will not waste time on looking for them.
Shine (Japanese: Seiso)
The objective of shinning is to maintain a work space neat and safe. Shining prevents machinery and equipment from deterioration. Working in a clean work space increases probability of noticing malfunctions in equipment machinery, such as leaks, vibrations, and breakages.
Standardize (Japanese: Seiketsu)
Once the first three phases are implemented, it is crucial to create a standard approach to maintain high standards of housekeeping and work space organization. In this phase sorting, straightening and shining duties are assigned to regular job responsibilities.
Sustain (Japanese: Shitsuke)
Sustain phase is about institutionalizing good practices and maintaining correct procedures. This phase is crucial for ensuring continuity of waste elimination efforts. Ultimate goal is to standardize effective production processes, so over time workforce develops and maintains effective work habits.
Read more:
