Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
Design For Six Sigma (DFSS) is a little different from the Six Sigma methodology. While when you're using the Six Sigma methodology, you try to simply improve the existing products, services, and processes, when you're using the DFSS you'll be redesigning an existing product, service, or process from scratch, or you'll be designing a new product, service or process.
A simple example of when you can use a Design For Six Sigma method is looking at an old school which still has all their records on paper. If the school wants to become more modern, they'll need to move all the data to a computer / database.
A simple example of when you can use a Design For Six Sigma method is looking at an old school which still has all their records on paper. If the school wants to become more modern, they'll need to move all the data to a computer / database.
There's no question that we live in a world where competition for services and products has never been higher. After all, consumers have a wide range of options like they never had before. So, it is natural that manufacturing companies keep trying to launch new and innovative services and products as well as to break into new markets.
The truth is that sometimes, companies manage to achieve success with a product or service. Other times, they don't. And when this happens, companies need to redesign the product, developing new iterations, testing them, and only then re-introduce them again to the market.
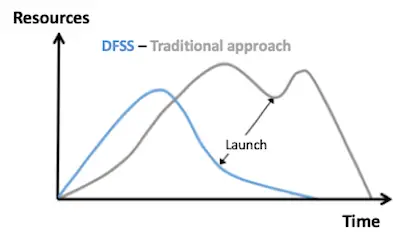
While this process seems normal and good, the reality is that is can not only be wasteful as well as expensive. Ultimately, companies' goal is to ensure that they get it right the first time. This means developing and launching a product that meets the actual needs and expectations of the customer. And this is exactly what Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) focuses on. This strategy focuses on doing all the research about customer's needs and expectations before the development and creation of the product itself. This way, companies don't only keep launching successful products as well as they can achieve higher levels of quality.
The truth is that sometimes, companies manage to achieve success with a product or service. Other times, they don't. And when this happens, companies need to redesign the product, developing new iterations, testing them, and only then re-introduce them again to the market.
While this process seems normal and good, the reality is that is can not only be wasteful as well as expensive. Ultimately, companies' goal is to ensure that they get it right the first time. This means developing and launching a product that meets the actual needs and expectations of the customer. And this is exactly what Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) focuses on. This strategy focuses on doing all the research about customer's needs and expectations before the development and creation of the product itself. This way, companies don't only keep launching successful products as well as they can achieve higher levels of quality.
What Is Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)?
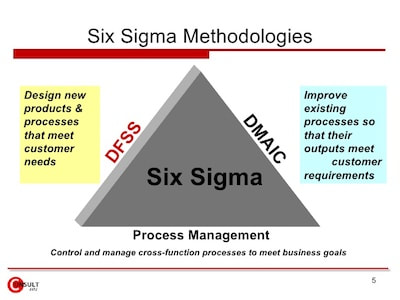
Simply put, Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is a different approach to process development or product creation. Even if you never heard about this methodology before, you probably already heard or read about the traditional Six Sigma that uses DMAIC or Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control methodology.
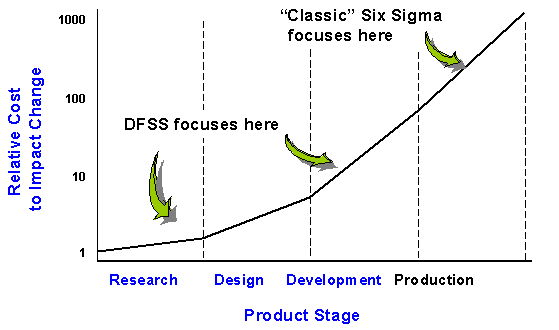
As you can imagine, both approaches are different. While the traditional six sigma tends to be most effective when used to improve the current process, the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)tends to be mainly used for the complete redesign of a process or product.
One of the things that you need to know about the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is that the steps this approach take depend on each company or organization. Some examples include DMADV, DCCDI, and IDOV.
As you can imagine, both approaches are different. While the traditional six sigma tends to be most effective when used to improve the current process, the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)tends to be mainly used for the complete redesign of a process or product.
One of the things that you need to know about the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is that the steps this approach take depend on each company or organization. Some examples include DMADV, DCCDI, and IDOV.
Notice that while the methodologies may be slightly different, the reality is that they all share the same goal: focus on fully understanding the needs of the customer and applying this information to the product and process design.
In what concerns to the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) methodology, in particular, you need to ensure that the DFSS team is cross-functional. After all, you need to consider all the different aspects of the product: the market research, the design, the process implementation, and the product launch. Ultimately, the main goal when you are using the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is to design processes and products while minimizing variations and defects at their roots.
In what concerns to the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) methodology, in particular, you need to ensure that the DFSS team is cross-functional. After all, you need to consider all the different aspects of the product: the market research, the design, the process implementation, and the product launch. Ultimately, the main goal when you are using the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is to design processes and products while minimizing variations and defects at their roots.
Why Should You Implement Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)?
There's no question that designing a new process or product takes both resources as well as time. Besides, it's important to keep in mind that many of today's products are highly complex. This means that things can go wrong in many different parts of the process.
If you think about it, whenever you develop a new product or process that doesn't meet your customer's needs and expectations, they won't be willing to pay for it. So, you will end up with a product that doesn't do you any good. However, when you use the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS), you will do the market research prior to the development of the new product. This means that when you are creating the product, you already know that it will actually fit many customers.
You can then see Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) as a proactive approach to design with quantifiable data and proven design tools that can improve your chances of success.
If you think about it, whenever you develop a new product or process that doesn't meet your customer's needs and expectations, they won't be willing to pay for it. So, you will end up with a product that doesn't do you any good. However, when you use the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS), you will do the market research prior to the development of the new product. This means that when you are creating the product, you already know that it will actually fit many customers.
You can then see Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) as a proactive approach to design with quantifiable data and proven design tools that can improve your chances of success.