Jidoka - Toyota Production System
The truth is that when we think about the Japanese people, we think about individuals who like to have everything in order and where nothing can be out of place. Maybe this is one of the reasons why Toyota Motor Corporation has always tried to improve their manufacturing process by adopting new methodologies.
Learn how you can apply Six Sigma to your organization.
Learn how you can apply Six Sigma to your organization.
In case you don't know, Toyota has adopted a lean manufacturing system or a Just-In-Time system that allows the company to be more efficient. In fact, the model was such a success that it was studied all over the world.
Toyota has its entire company focused on "making the vehicles ordered by customers in the quickest and most efficient way, in order to deliver the vehicles as quickly as possible." With this in mind, the company is using the Jidoka Toyota, which can be simply translated as the automation via the human touch, in conjunction with the concept of Just-In-Time. With the implementation of the Jidoka Toyota, the company has its own way to operate. When a problem suddenly arises, the equipment will be immediately stopped. The main goal of this interruption is to ensure that the company doesn't produce any defective products. On the other hand, with the implementation of the Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology, Toyota uses one process for only what is needed by the following process. Overall, this is how the TPS Toyota works so that the company can produce high-quality vehicles quickly and efficiently, one at a time, that can make their customers completely happy.
Discover what is a Gemba Board.
Here's a more in-depth look over the TPS Toyota and of the two components it includes:
Discover what is a Gemba Board.
Here's a more in-depth look over the TPS Toyota and of the two components it includes:
#1: Jidoka:
The main principle behind Jidoka is that quality is key and needs to be present during the manufacturing process. After all, with Jidoka, you can easily visualize the problems that occur.
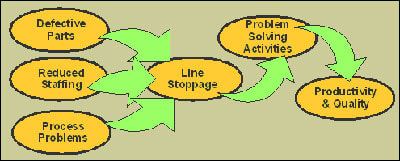
When a machine detects a problem and stops on its own preventing defective products to be produced, this problem will be immediately communicated via the Andom system.
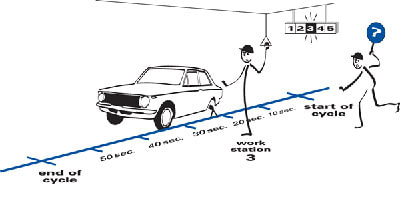
One of the best things about the TPS Toyota is that since their vehicles are made one by one, the interruption of a process won't affect the next one. SO, workers can continue to do their jobs using another machine while they prevent what caused the machine to break or stop in the first place.
Discover more about the Andon System.
When a machine detects a problem and stops on its own preventing defective products to be produced, this problem will be immediately communicated via the Andom system.
One of the best things about the TPS Toyota is that since their vehicles are made one by one, the interruption of a process won't affect the next one. SO, workers can continue to do their jobs using another machine while they prevent what caused the machine to break or stop in the first place.
Discover more about the Andon System.
#2: Just-in-Time:
The main goal of the Just-in-Time methodology is to improve the overall productivity of an organization by making only "what is needed, when it is needed, and in the amount needed!"
So, according to the Just-in-Time principle, the goal is to produce high-quality products by eliminating unreasonable requirements, inconsistencies, and waste on the production line.
Learn more about the Hoshin Kanri planning.
So, according to the Just-in-Time principle, the goal is to produce high-quality products by eliminating unreasonable requirements, inconsistencies, and waste on the production line.
Learn more about the Hoshin Kanri planning.
With the combination of these two methodologies, the TPS Toyota seems to be one that performs well. It doesn't only produce quality products only as well as they also increase the productivity by eliminating all the waste in the production line. In addition, even when a problem occurs and a process needs to stop until the root causes are discovered and the solution found and implemented, this won't stop the next processes from continuing to work regularly.



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed